Description
The motor from a 3.5″ floppy disk drive. The coils, arranged radially, are made from copper wire coated with blue insulation. The well balanced rotor (upper correct) has been taken out and turned upside-down. The grey band inside its glass is a long lasting magnet.
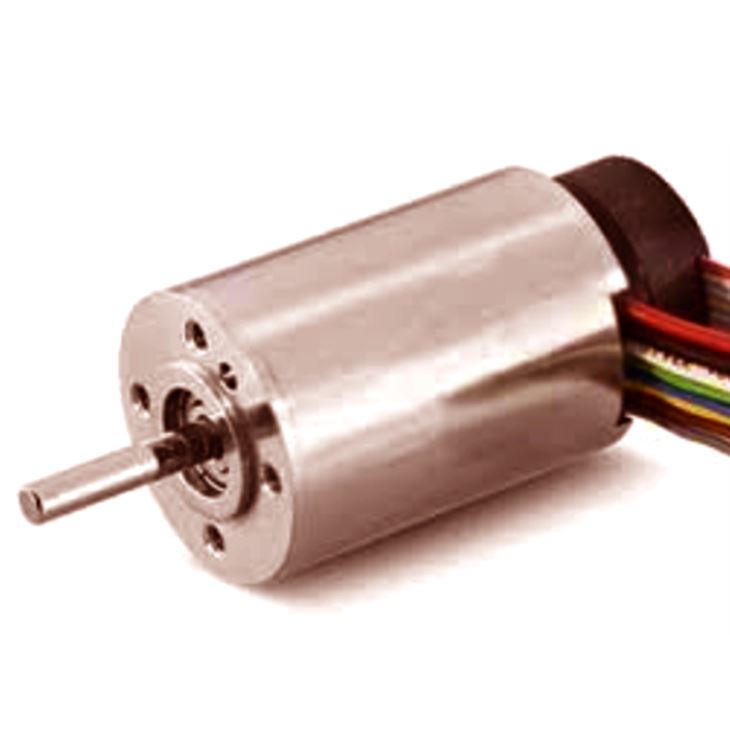
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC motor or BL electric motor), also called electronically commutated electric motor (ECM or EC engine) and synchronous DC motors, are synchronous motors powered by DC electricity via an inverter or switching power supply which creates an AC electric current to drive each phase of the motor with a closed loop controller. The controller provides pulses of current to the motor windings that control the rate and torque of the motor.
The construction of a brushless motor system is normally similar to a long term magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), but may also be a switched reluctance electric motor, or an induction (asynchronous) motor
The advantages of a brushless electric motor over brushed motors are high power to weight ratio, high speed, electronic control, and lower maintenance. Brushless motors discover applications in such areas as computer peripherals (disk drives, printers), hand-held power tools, and vehicles ranging from model aircraft to automobiles.
In an average DC motor, there are permanent magnets externally and a spinning armature on the inside. The long term magnets are stationary, therefore they are known as the stator. The armature rotates, so that it is named the rotor.